TypeORM NodeJS many to many relation
The features that use many to many relationships were built easier on nowaday by implementing the library TypeORM in NodeJS.
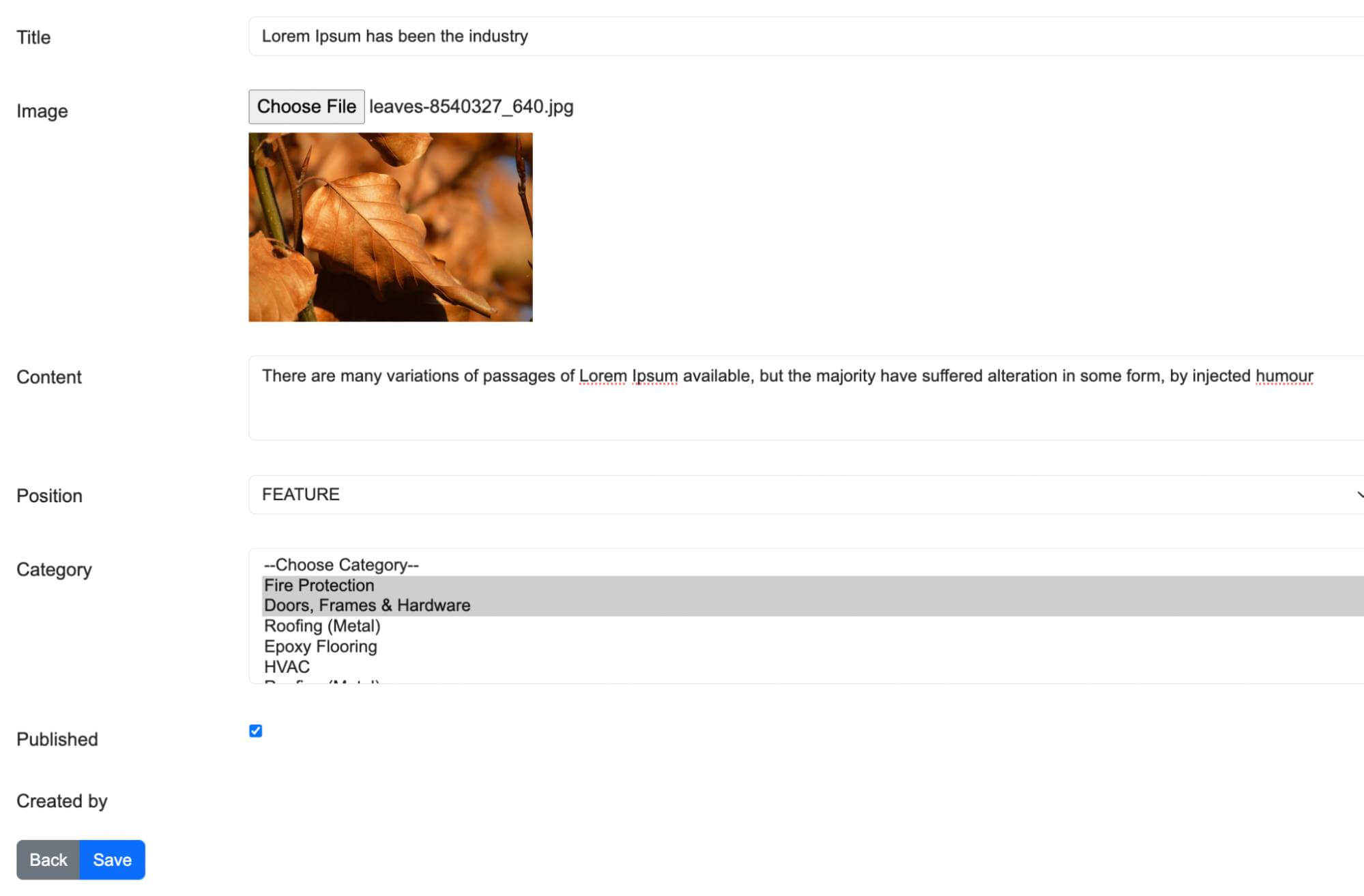
I want to show you an example about many to many relationships. When we build a feature blog website, it will have the posts and belong to categories. A post can have many categories and a category can belong to some posts. As in the image below, you can choose one or two categories when you edit a post.
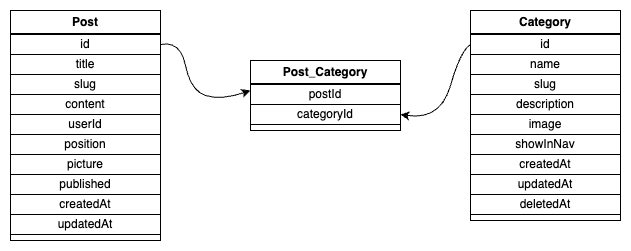
To do this, you must have 3 tables in the database. One for post, one for category and the last table contains the relationship of 2 tables post and category. And we will call it the posts_categories, this table will have 2 columns: post_id and category_id.
We will use the express framework and typeORM to build this example.
For installing the express framework on the link below https://expressjs.com/en/starter/installing.html. And TypeORM is in https://typeorm.io/#installation.
Model
After installing, we will create the model for the category table. We will located it in to the directory /src/core/category/CategoryMode.ts
@Entity()
export class CategoryModel extends BaseEntity
{
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column()
name: string;
@Column()
slug: string;
@Column('text')
description: string;
@Column({ nullable: true })
image: string;
@Column({ default: true })
showInNav: boolean = true;
@CreateDateColumn()
createdAt: Date;
@UpdateDateColumn()
updatedAt: Date;
@DeleteDateColumn()
deletedAt: Date;
}
For model of table post, it will located at /src/core/Post/PostModel.ts
@Entity()
export class PostModel extends BaseEntity
{
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column()
title: string;
@Column()
slug: string;
@Column('text')
content: string;
@Column({ default: true })
published: boolean = true;
@Column({ length: 16, default: '' })
position: string;
@Column()
picture: string;
@CreateDateColumn()
createdAt: Date;
@UpdateDateColumn()
updatedAt: Date;
@ManyToOne(() => UserModel, (user) => user.posts)
user: UserModel;
@ManyToMany(() => CategoryModel)
@JoinTable()
categories: CategoryModel[];
}
Now, the important thing is to declare many to many relationships as below.
@ManyToMany(() => CategoryModel)
@JoinTable()
categories: CategoryModel[];
Datasource
After that, you need to define a DataSource of TypeORM and connect it to the database. I will use MySql in this project. And located it on the directory /src/infrastructure/repositories/dataSource/AppDataSource.ts
import "reflect-metadata"
import { DataSource } from "typeorm"
import { PostModel } from "../../../core/post/PostModel";
import { UserModel } from "../../../core/user/UserModel";
import { CategoryModel } from "../../../core/category/CategoryModel";
const path = require('path');
const process = require('process');
const rootPath = path.resolve('./');
const env = process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development';
const config = require(rootPath + '/config/config.json')[env];
export const AppDataSource = new DataSource({
type: config.dialect,
host: config.host || 'localhost',
port: config.port || 3306,
username: config.username,
password: config.password,
database: config.database,
entities: [
PostModel,
UserModel,
CategoryModel
],
// logging: true,
synchronize: true,
});
AppDataSource.initialize()
.then(() => {
console.log("Data Source has been initialized!")
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error("Error during Data Source initialization", err)
})
On the Datasource object, we need to connect the PostModel and CategoryModel to this DataSource. When you run the project, it will create tables for the models that we defined above automatically.
Repository
Now, let's create a repository and controller to display the data from the model. For repository of the PostModel, it will locate at /src/core/post/PostRepository.ts
import { PostRepositoryInterface } from "./PostRepositoryInterface";
import { PostModel } from "./PostModel";
import { GenericRepository } from "../../infrastructure/repositories/generic/GenericRepository";
import { AppDataSource } from "../../infrastructure/repositories/dataSource/AppDataSource";
import { PostPosition } from "./PostPosition";
export class PostRepository extends GenericRepository implements PostRepositoryInterface
{
constructor() {
super(AppDataSource.getRepository(PostModel));
}
getLatest(total: number): Promise {
return this.repository.find({
relations: ['categories'],
order: {
id: "DESC",
},
take: total
});
}
getFeature(total: number): Promise { }
findByIdIncludeUser(id: number): Promise { }
}
You can get the repository of PostModel on the Datasource by line below:
AppDataSource.getRepository(PostModel);
To get all the records on the post table you can use the function
this.repository.find();
Or you can get by pagination
this.repository.findAndCount({
take: take ?? 10,
skip: skip ?? 0
});
Also, you will need to get the data by filtering specific columns and paginating the results. You need to define a variable as FindManyOptions like below
getFindOptions(): FindManyOptions
{
const limit:number = this.getLimit() ?? 10;
const page:number = this.getPage() > 0 ? this.getPage() : 1;
let whereClauses = {}
if (this.getName() !== undefined) {
whereClauses.name = Like(`%${this.getName()}%`);
}
if (this.getDescription() !== undefined) {
whereClauses.description = Like(`%${this.getDescription()}%`);
}
if (this.getShowInNav() !== undefined) {
whereClauses.showInNav = this.getShowInNav();
}
const findOptions: FindManyOptions = {
take: limit,
skip: (page - 1) * limit,
where: whereClauses
};
return findOptions;
}
And passing this param to the function findAndCount
this.repository.findAndCount(filter.getFindOptions());
Controller
With the controller for responding data of the table post, it will be located at /src/app/controllers/PostController.ts.
On the controller, you just need to call the functions that you defined on the repository. For the example, this action will get latest 10 records on the post table.
getLatest()
{
const results = this.postRepository.getLatest(10);
this.jsonResponse(results);
}
When you request this action, it will respond to the records of the post table including the categories belonging to each post if you add the param relations to function find of repository like this.
getLatest(total: number): Promise {
return this.repository.find({
relations: ['categories'],
order: {
id: "DESC",
},
take: total
});
}
You can see the json response like the below image
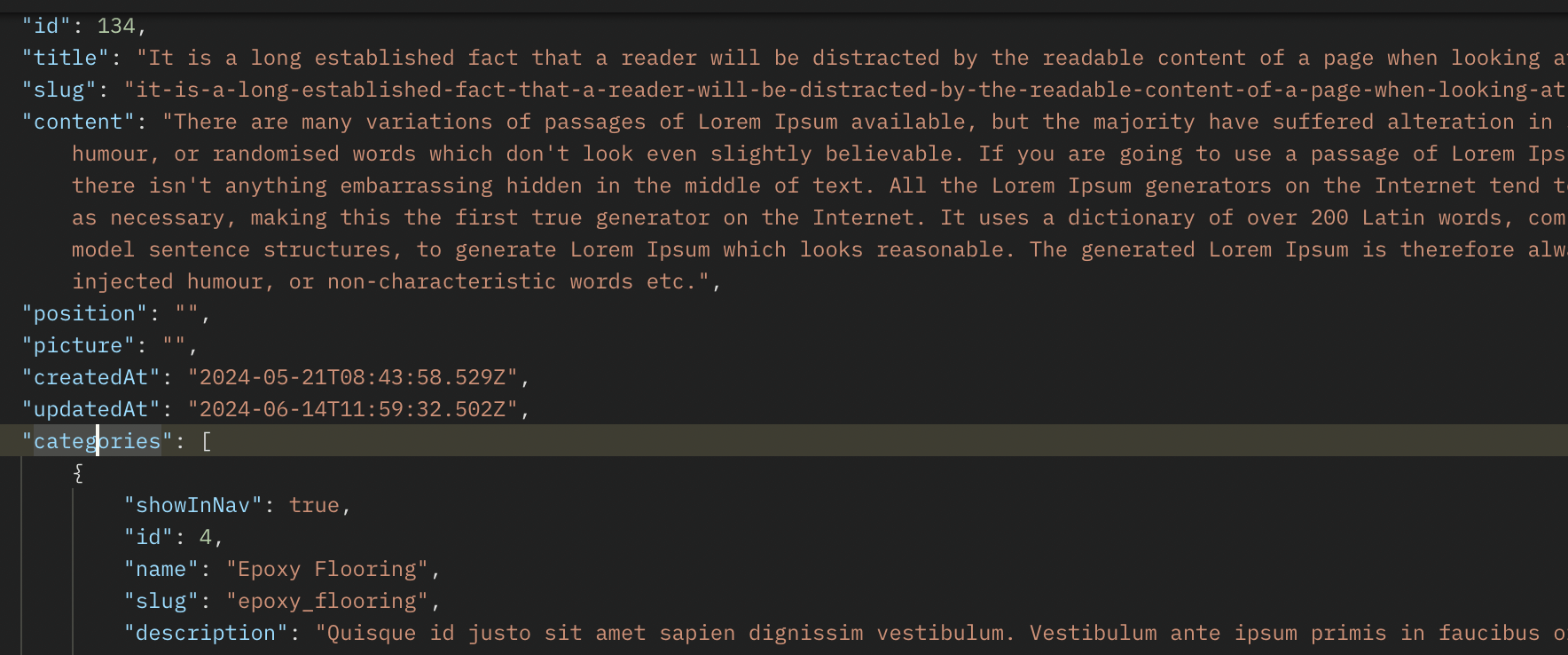
Create or update the post with categories
If you want to create or update items that have related many to many relationships, it is very easy with TypeORM. You just send the related objects and the model will identify they are the related objects and insert or update records in the related table. You don't need to write any more code for updating this.
You need to use the below function for inserting or updating a post.
save(item: T): Promise {
return this.repository.save(item);
}
In the controller, I call the function above like this.
const post: Promise = this.postRepository.save(body);
And the body of data that I was sent is the below image. Each values of categories param is a category object.
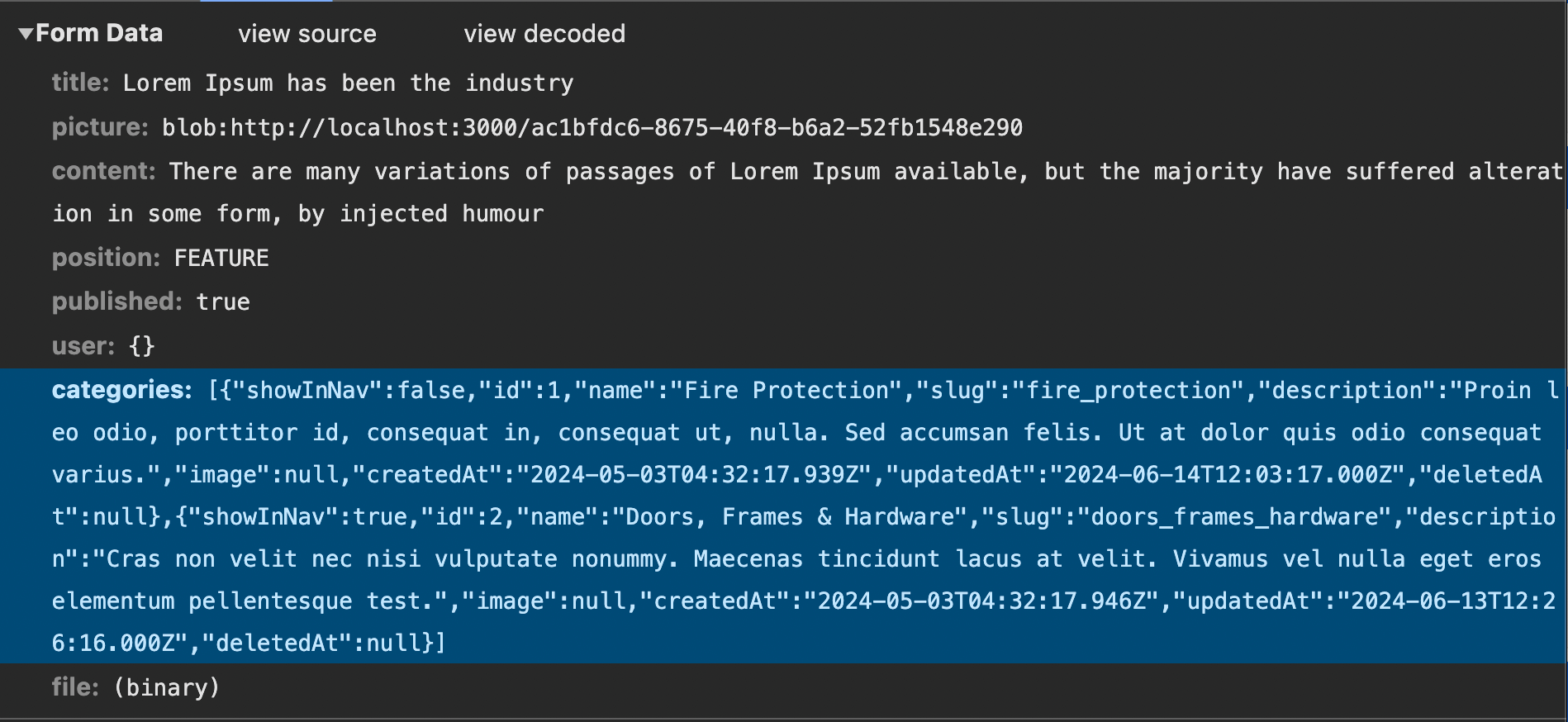
Conclude
If you use the library for your project, you will save many times
to query the records in the database. Also, the source code
is short and easy to maintain or upgrade projects. You can
find the full source code on my github on below link:
https://github.com/luan4637/node-vue-blog